Knee Osteoarthritis: Don’t Compromise Your Mobility – Seek Treatment Today
Understanding Knee Osteoarthritis
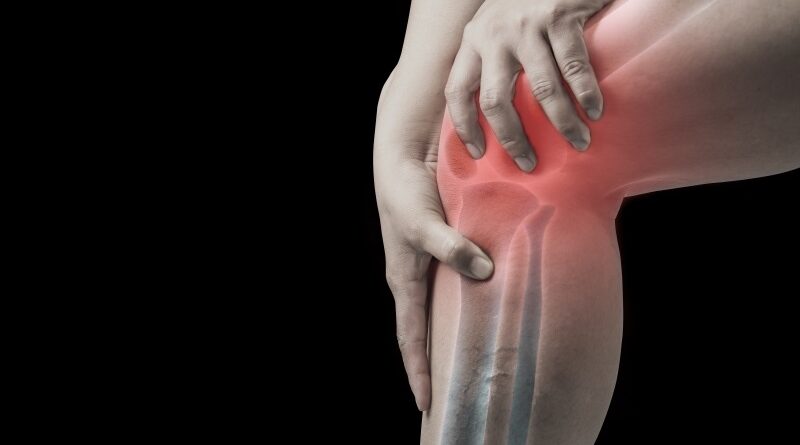
Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the deterioration of cartilage in the knee joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and functional impairment. Often regarded as one of the most prevalent forms of arthritis, it primarily affects older adults but is increasingly being recognized in younger populations, particularly those with risk factors such as obesity and genetic predispositions. As the cartilage wears down, the bones may begin to rub against each other, causing inflammation and further enhancing the discomfort experienced by individuals.
The onset of knee osteoarthritis can be attributed to various contributing factors. Age is a significant factor, as the likelihood of developing this condition increases over time due to the natural aging process and cumulative wear and tear on the joints. Excess body weight is another critical factor; additional pressure on the knee joints can accelerate cartilage breakdown. Genetics also plays a notable role, as familial patterns of osteoarthritis indicate a hereditary component. Other potential factors include previous injuries to the knee, such as fractures or ligament tears, which can predispose individuals to develop this condition later in life.
Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis often manifest gradually and can vary in intensity, encompassing pain during movement, a sense of stiffness particularly after prolonged periods of inactivity, and noticeable swelling around the joint. These symptoms can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily activities, leading to limitations in mobility and overall quality of life. Recognizing the early signs of knee osteoarthritis is vital for effective management, as timely intervention can slow disease progression and help maintain mobility. Early detection often involves consulting healthcare professionals who can provide a comprehensive assessment and appropriate treatment options tailored to the individual’s needs.
Impact of Knee Osteoarthritis on Mobility
Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that profoundly affects mobility and daily activities. As the cartilage in the knee joint gradually deteriorates, individuals often experience significant knee pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can severely limit mobility. Simple tasks that were once taken for granted, such as walking, climbing stairs, or standing up from a seated position, can become increasingly challenging. The pain associated with knee osteoarthritis may deter individuals from engaging in physical activities, leading to a further decline in their functional capabilities and overall health.
Walking, an essential component of daily life, can become a daunting task for those suffering from knee osteoarthritis. The discomfort and instability in the knee can make even short distances feel overwhelming, often resulting in reduced physical activity. Climbing stairs poses another challenge, as the repetitive motion can exacerbate pain and increase the risk of falls. Consequently, many individuals may opt to avoid stairs altogether, which can further limit their mobility and independence.
Participating in recreational activities, which are crucial for maintaining a healthy, enjoyable lifestyle, also becomes increasingly difficult due to knee osteoarthritis. Hobbies that involve physical exertion, such as jogging, hiking, or sports, may be sidelined, leading to feelings of frustration and helplessness. This restriction can negatively impact mental well-being, contributing to feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression. The emotional toll of these physical limitations can diminish the overall quality of life for those affected.
In essence, knee osteoarthritis not only imposes physical limitations but also creates significant emotional challenges. Understanding the far-reaching impacts of this condition can help emphasize the importance of seeking timely treatment and support. Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects is crucial for preserving mobility and enhancing overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint condition, requires a multifaceted approach for effective management and treatment. The initial step often includes conservative methods that focus on alleviating pain and improving joint function. Physical therapy is a cornerstone of conservative treatment, as it enhances strength, flexibility, and endurance in the muscles surrounding the knee. Tailored exercise programs can help individuals maintain mobility without exacerbating the condition.
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as excess weight places additional strain on the knee joints, leading to increased pain and discomfort. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can also contribute positively to overall joint health. Furthermore, incorporating low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling can help in preserving joint function without putting undue stress on the knees.
Pain relief medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics, may be recommended to manage discomfort effectively during daily activities. These medications can offer temporary relief and improve the quality of life for those affected by knee osteoarthritis.
For individuals who do not achieve satisfactory relief through conservative approaches, advanced treatment options are available. Injections of corticosteroids can provide temporary relief from inflammation, while hyaluronic acid injections can enhance joint lubrication and reduce pain. In cases where joint deterioration is severe, surgical interventions such as arthroscopy in Delhi may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or bone spurs. Ultimately, knee replacement surgery in Delhi is considered when other treatments have proven ineffective, offering a potential return to improved mobility.
Understanding these treatment options empowers individuals with knee osteoarthritis to actively participate in their care, making informed decisions that align with their specific health needs and lifestyle goals.
The Importance of Seeking Treatment Early
Early intervention in the management of knee osteoarthritis is crucial for preserving mobility and enhancing overall quality of life. This degenerative condition can lead to severe pain, stiffness, and reduced function, significantly affecting daily activities. When symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, or limited range of motion present themselves, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals promptly. Delaying treatment can result in the progression of the disease, leading to more extensive joint damage and more complex treatment options down the line.
One of the primary advantages of early treatment is the potential to slow the progression of knee osteoarthritis. Various conservative management strategies, such as physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and medication, can be more effective when initiated early. These options can help manage symptoms, enhance joint function, and mitigate further damage. Engaging in a structured exercise regimen and maintaining a healthy weight can also play critical roles in managing knee health and should be part of an early intervention strategy.
An additional benefit of seeking early treatment is the opportunity for better pain management. Effective symptom control can lead to improved mobility, enabling individuals to engage in daily activities and social interactions that are important for emotional well-being. By addressing the condition early, patients are often able to prevent the development of secondary issues, such as muscle weakness or loss of function, which can compound the challenges posed by knee osteoarthritis.
In conclusion, the importance of early treatment cannot be overstated. Recognizing the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis and consulting with orthopaedic in Dwarka without delay is vital. Timely intervention can dramatically influence the trajectory of the disease, allowing individuals to maintain mobility and lead fulfilling lives. By prioritizing early care, individuals can support their joint health and enhance their overall well-being.